Gynecologic oncologists diagnose and treat all gynecologic cancers, including cancers of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, vagina, cervix, and vulva, in addition to a wide range of complex gynecology issues.
At the WVU Cancer Institute, we have the largest gynecologic oncology team in West Virginia. Our four fellowship-trained, board-certified or board-eligible physicians utilize a full range of treatments, including immunotherapy, chemotherapy, minimally-invasive and robotic-assisted surgery, and clinical trials to create individual treatment plans for each patient.
We use molecular testing and biomarkers to guide our recommendations for treatment. Our goal is to provide the most up-to-date, evidence-based care available.
The team also includes two specialized nurse practitioners, gynecologic oncology physician assistants, and obstetrics and gynecology resident physicians, as well as nurse navigators, social workers, an oncology-certified pharmacist, and chaplain. A pain management specialty group and counselor are also available to support our patients’ needs. And we work closely with WVU Medicine radiation oncologists and hematologic oncologists throughout the state and region.
We understand that many of our patients drive long distances to receive care, so our team works hard to coordinate care and optimize each visit.
Types of Gynecologic Cancers and Complex Gynecologic Conditions We Treat
We specialize in the evaluation and treatment of cancerous and noncancerous tumors affecting women’s reproductive organs.
We treat all types of gynecologic cancers, including:
Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer can be found early through regular screening tests. It starts in the cells lining your cervix and develops most often in women over age 30. Although HPV is the most common cause of cervical cancer, it’s not the only cause.
Ovarian, primary peritoneal, and fallopian cancer
Ovarian cancer predominately starts in the ovaries, but it can also be found to arise from the fallopian tubes or the peritoneum (tissue lining covering the organs in your abdomen).
Uterine cancer (including endometrial cancer)
There are two different types of uterine cancer — uterine sarcomas and endometrial cancer. Uterine cancer starts in the uterus.
Vaginal cancer
This type of cancer is found in the vagina. It’s very rare and is more often found in women over age 60.
Vulvar cancer
This rare type of cancer is mostly diagnosed in older women and is cancer found on the outer surface area of female genitals, the vulva. Vulvar cancer usually starts as a lump or sore on the vulva that often causes itching.
Complex gynecologic conditions
Our team also treats cervical, vaginal and vulvar pre-cancerous lesions and, ovarian and uterine masses, and performs complex robotic hysterectomies.
Diagnosing Gynecologic Cancer
There are different ways to diagnose gynecologic cancer, and it’s important for you to talk with your doctor if you notice any new symptoms such as pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding or discharge, pain in the back or stomach, or itching or burning in the vulva. If your doctor suspects you have cancer, they may order certain tests to make a diagnosis.
- Advanced imaging — Doctors use ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and positron emission tomography (PET) scans to detect signs of disease and see whether cancer has spread to other areas of the body, such as the lymph nodes.
- Biopsy — Doctors use this test to examine tissue under a microscope to determine whether cancer is present. During a biopsy, a doctor removes a small sample of tissue at the tumor site to analyze in a lab. Biopsy results help oncologists plan the best treatment for you. There are several different biopsy types, including image-guided biopsy, fine-needle aspiration biopsy, core needle biopsy, and excisional and endoscopic biopsy.
- Pap test — Doctors remove cells from your cervix to view under a microscope. The test looks for cancerous or abnormal cells that may progress to cancer without treatment.
- Transvaginal ultrasound — Doctors perform this ultrasound through the vagina. Using an ultrasound probe, a doctor will insert the probe about two or three inches into your vaginal canal to take images.
Treatment for Gynecologic Cancer
From your first visit, our team works with you to address your specific condition and needs.
Your care plan may include:
- Infusion therapy — Our doctors give medicine and fluids through a catheter into your bloodstream. Medicines may include antibiotics, chemotherapy, and fluids to build nutrients.
- Systemic treatment — Systemic treatment includes chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and hormone therapy. Our doctors use the latest in anti-cancer medicine to destroy cancer cells. We also use medicines to slow cancer growth and shrink tumors before surgery. Sometimes, we use medication alongside other treatments such as radiation or after surgery to destroy any cancer cells that might remain. In addition to these standard treatments, we also offer patients access to some of the latest clinical trials available to women with gynecologic cancer.
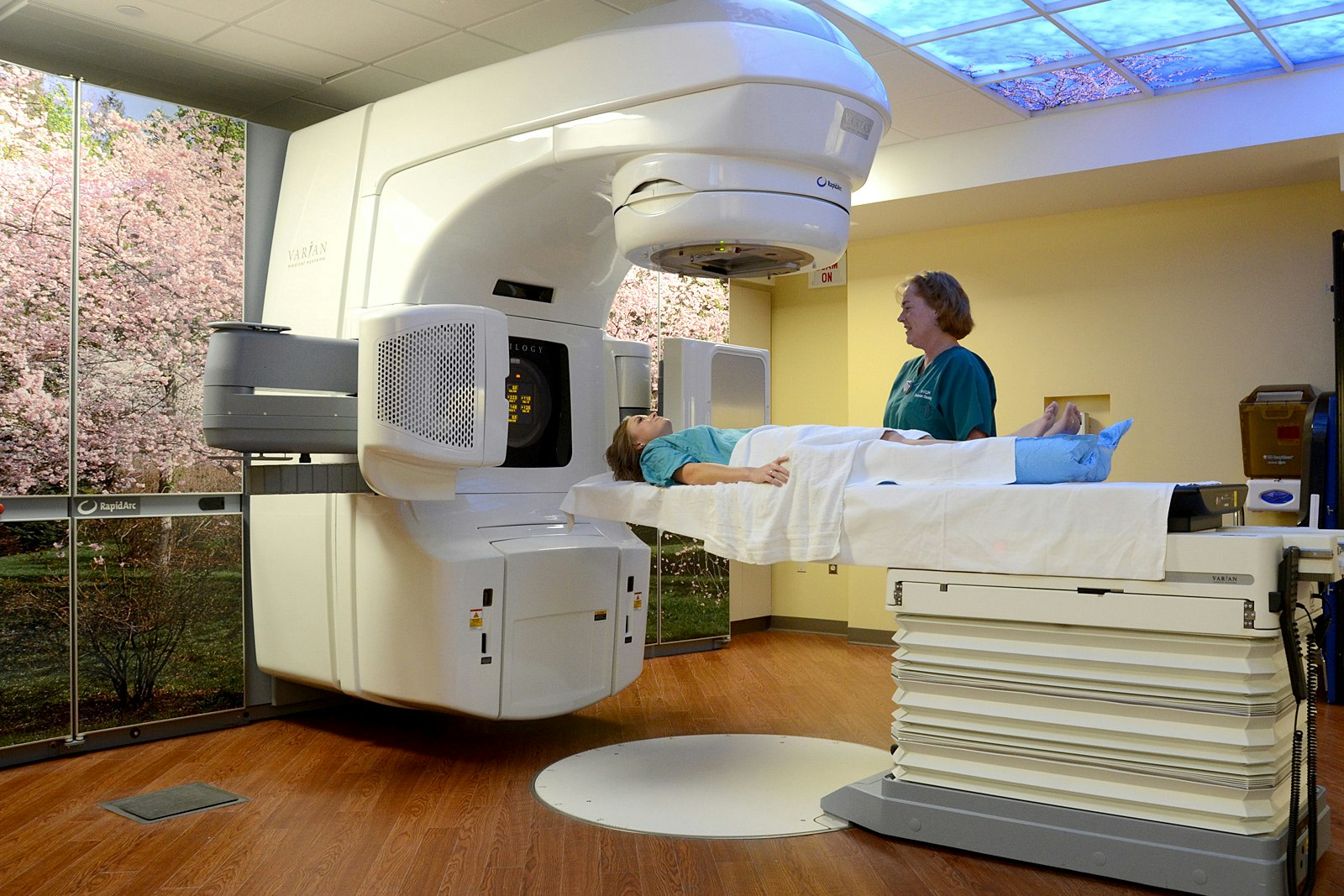
- Radiation — We use radiotherapy treatments to target, destroy, and shrink many types of cancers. The treatments use a linear accelerator to produce precise, high-energy rays that target the exact area of cancer and spare healthy cells. Radiation oncology includes 3D conformal radiotherapy, image-guided radiation therapy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy, and brachytherapy. We offer advanced hybrid interstitial brachytherapy for patients with gynecologic cancers. This state-of-the-art treatment combines intracavitary and interstitial techniques to deliver highly targeted radiation directly to the tumor while minimizing exposure to healthy tissue. It is especially effective for complex or locally advanced cases, offering improved tumor control and fewer side effects.
- Surgery — Surgery may help us diagnose, stage, and treat many tumors. Surgical options for gynecologic cancer include advanced robot-assisted surgery, laparoscopy, and open incision surgery for the uterus, cervix, and ovary cancers. We also treat women without cancer who need complex surgical care.
Resources for Gynecologic Cancer
We believe cancer care goes beyond diagnosis and treatment. Many resources are available to answer questions and connect you with others, including: